SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an internet protocol used in network management systems to monitor network-attached devices such as computers, servers, routers, switches, gateways, wireless access points, VoIP phones, and etc. for conditions that warrant administrative attention.
In Windows Server 2016, an SNMP service is still available. You can set it up to provide a way to monitor various resources remotely on a Windows Server 2016 machine. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an age-old network monitoring protocol still in wide use today. For Windows Server, you need an agent, not a collector (or server). For example, Solarwinds syslog server (formerly Kiwi syslog server) is a syslog server, not a syslog agent. If you don’t have a syslog server already, then that is a good option for general use or vCenter Log Insight is a good option if you are already using VMware vSphere. I have to configure the security settings for the SNMP-Service on a Windows Server. But they are missing! Here are the facts: OS: Windows Server 2012 R2. I installed the SNMP feature and I believe, that I already configured the service (but I forgot to add another IP under Security tab).
SNMP provides management data in the form of variables on the managed systems, which describe the system configuration parameter or current status value. These variables can then be read and queried (or sometimes set or write) by managing applications.
Windows system, including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 (R2), Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 (R2), Windows 10, Windows Server 2016, either does not have SNMP service installed by default, or does not turn on SNMP service by default, or does not configure SNMP service by default, thus users need to manually install, enable or configure SNMP service before they can monitor the system via SNMP.
Windows Server 2012 Snmp Settings Windows 7
Note that you must be logged on as an administrator or a member of the Administrators group in order to complete this procedure. If your computer is connected to a network, network policy settings may also prevent you from completing this procedure.
How to Install and Enable the SNMP Service
- In Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, click Start button, then go to Control Panel and run Add or Remove Programs applet. On Add or Remove Programs dialog, click Add/Remove Windows Components to open “Windows Components” wizard.
In Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2, click Start button, then go to Control Panel. Click on Programs ->Programs and Features link and then click on Turn Windows features on or off. If you’re prompted with User Account Control dialog, click “Continue”.
In Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 or later, open the Control Panel, then click or tap on Programs ->Programs and Features link, followed by Turn Windows features on or off. If you’re prompted with User Account Control dialog, click “Continue” or “Yes”.
- In Components of Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, click on the Management and Monitoring Tools (make sure that you do not select or clear, tick or untick its check box to change the existing selection), and then click Details.
- Select and tick the check box of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), Simple Network Management Protocol or SNMP feature.
- Click OK. In Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, you need to click additional Next button.
SNMP service will be installed on the system. You may require to insert the Windows setup CD/DVD disc into optical drive.
- SNMP will start automatically after installation. But it’s recommended to verify the service status from Services in Control Panel or Task Manager, and if it’s stopped, you can start the SNMP service from there.
Two new services will be created:
- SNMP Service which is the main engine with agents that monitor the activity in the network devices and report the information to the monitoring console workstation.
- SNMP Trap Service which receives trap messages generated by local or remote SNMP agents and forwards the messages to SNMP management programs running on this computer.
Windows doesn’t assign any community string to the SNMP service by default, and also only allow access from localhost (this computer only) or local devices. Further configuration is needed to add in desired community string, which act as the password to grant reply to any SNMP request from remote system.
How to Configure Security Community String for SNMP Service
Note: The following guide public community string as example.
- Open Control Panel.
- In Windows XP, go to Performance and Maintenance, while the other versions of Windows, System and Maintenance link.
- Open Administrative Tools.
- Run Services applet.
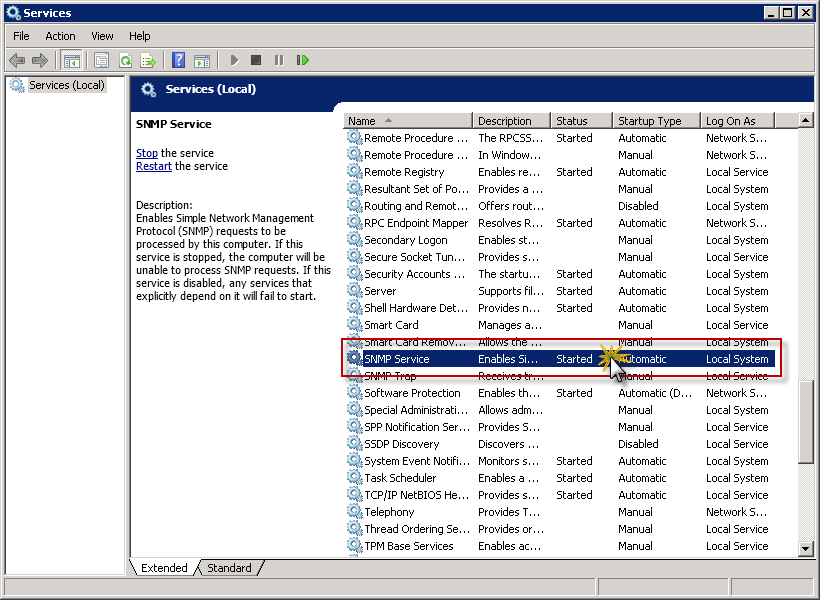
- Locate and right click on SNMP Service, then select Properties.
- In SNMP Service Properties window, click on Services tab.
- Under “Accepted community names” section, click Add button.
- Select the appropriate permission level for the community string in the “Community Rights” drop down list to specify the authentication that the host used to process and grant SNMP requests from the selected community. Normally READ ONLY is recommended.
- In the “Community Name” box, type public or any case-sensitive community name that you want.
- Click on Add button.
- In order for the SNMP service to accept and receive SNMP request packets from any host on the network, including external remote host regardless of identity, click Accept SNMP packets from any host.
To limit the acceptance of SNMP packets, click Accept SNMP packets from these hosts, and then click Add, and then type the appropriate host name, IP or IPX address in the Host name, IP or IPX address box. You can restrict the access to local host or limited servers only by using this setting. Finish off by clicking Add button again.
- Click OK when done. Note that you may need to reboot for the settings to take effect.
Optionally, if you requires to send SNMP traps to remote trap destination, you can configure it at the “Traps” tab.
How to Configure SNMP Traps
- Open Control Panel.
- In Windows XP, go to Performance and Maintenance, while the other versions of Windows, System and Maintenance link.
- Open Administrative Tools.
- Run Services applet.
- Locate and right click on SNMP Service, then select Properties.
- Go to Traps tab.
- In SNMP Service Properties window, click on Traps tab.
- In the “Community name” text box, enter public or any other case-sensitive SNMP community name to which this computer will send trap messages.
- Click on Add to list button.
- Then, click or tap on the Add button below “Trap destinations” to enter IP addresses, host names or IPX addresses of the remove server that will receive SNMP traps.
Applies To: Windows Server 2012
The following is a list of features and functionalities in Windows Server® 2012 that have either been removed from the product in the current release or are planned for potential removal in subsequent releases. It is intended for IT professionals who are updating operating systems in a commercial environment. This list is subject to change in subsequent releases and may not include every deprecated feature or functionality.
Features removed from Windows Server 2012
The following features and functionalities have been removed from this release of Windows Server 2012. Applications, code, or usage that depend on these features will not function in this release unless you employ an alternate method.
Active Directory Federation Services
Support for applications that use the “NT Token mode” configuration of the web agent is removed. Applications are expected to move to Windows Identity Foundation and use the “Claims to Windows Token Service” to convert a UPN from a SAML token to a Windows token for consumption in the application.
Support for “Resource Group” is removed. (Resource groups are explained at http://technet.microsoft.com/library/cc753670(WS.10).aspx)
Support for using Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) as an authentication store is removed
You are required to migrate to the AD FS version in Windows Server 2012. In-place upgrade from AD FS 1.0 or “out of box” AD FS 2.0 is not supported.
Server Core components
Oclist.exe has been removed. Instead, use Dism.exe. For documentation on using Dism.exe, see http://technet.microsoft.com/library/dd772580(WS.10).aspx.
Clustering
The Cluster Automation Server (MSClus) COM application programming interface (API) has been made an optional component called FailoverCluster-AutomationServer which is not installed by default. Cluster programmatic functionality is now provided by the Failover Cluster API and the Failover Cluster WMI provider.
The Cluster.exe command-line interface has been made an optional component called FailoverCluster-CmdInterface which is not installed by default. Cluster command-line functionality is provided by the Failover Cluster PowerShell cmdlets.
Support for 32-bit cluster resource DLLs has been deprecated. Use 64-bit versions instead.
Graphics
Support for hardwire drivers for XDDM has been removed. As a result, XDDM graphics drivers will not load in Windows Server 2012. Instead, you can do any of the following:
Use the WDDM “basic display-only driver” included in the operating system.
Use a WDDM “display-only driver” provided by a hardware vendor.
Use a full WDDM driver provided by a hardware vendor.
Support for native VGA via the PC/AT BIOS is removed. The WDDM “basic display-only driver” included in the operating system will replace this functionality. In UEFI systems, you may see fewer high-resolution (VESA) modes, but there is no other impact.
Hyper-V
VM Chimney (also called TCP Offload) has been removed. The TCP chimney will not be available to guest operating systems.
Support for Static VMQ has been removed. Drivers using NDIS 6.3 will automatically access Dynamic VMQ capabilities that are new in Windows Server 2012.
Networking
NetDMA has been removed.
Support for Token Rings has been removed.
Server roles
The Role Collector (Ceiprole.exe) and the associated API (Ceiprole.dll) have been removed. To collect telemetry data on server roles, use Server Manager.
Server Message Block
SMB.sys has been removed. The operating system now uses the Winsock Kernel (WSK) to provide the same functionality.
SQL Server
Versions of Microsoft SQL Server prior to 7.0 are no longer supported. Computers running Windows Server 2012 that connect to computers running SQL Server 6.5 (or earlier) will receive an error message.
Storage
The Storage Manager for SANs snap-in for MMC has been removed. Instead, manage storage with PowerShell cmdlets and Server Manager.
The Storage Explorer snap-in for MMC has been removed.
The SCSIport host-bus adapter driver has been removed. Instead, either use a Storport driver or a different host-bus adapter.
Visual Studio
Windows Server 2012 Snmp Settings
Support for Visual Studio Analyzer 2003 over ODBC, OLEDB, and ADO has been removed.
Windows Help
The Windows Help program (specifically, WinHlp32.exe, the executable file that opens *.hlp help files) has been removed from Windows since Windows Server 2008. Previously, downloadable packages that provide this functionality were made available (see http://support.microsoft.com/kb/917607). Starting with this release, no download will be provided to enable you to view *.hlp files on Windows Server 2012. For this milestone release, Windows Help is also currently unsupported in Windows® 8.
Features deprecated starting with Windows Server 2012
The following features and functionalities are deprecated starting with this release. Eventually, they will be completely removed from the product, but they are still available in this release, sometimes with certain functionality removed. You should begin planning now to employ alternate methods for any applications, code, or usage that depend on these features.
Active Directory
Dcpromo.exe has been deprecated. In Windows Server 2012, if you run dcpromo.exe (without any parameters) from a command prompt, you receive a message directing you to Server Manager, where you can install Active Directory Domain Services using the Add Roles wizard. If you run dcpromo /unattend from a command prompt, you can still perform unattended installations that use Dcpromo.exe. This allows organizations to continue to use automated Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) installation routines based on dcpromo.exe until they can rewrite those routines using Windows PowerShell. For more information, see http://technet.microsoft.com/library/hh472160.aspx.
Database management systems
ODBC support for 16- and 32-bit applications and drivers is deprecated. Use 64-bit versions instead.
ODBC/OLEDB support for Microsoft Oracle is deprecated. Migrate to drivers and providers supplied by Oracle.
Jet Red RDBMS and ODBC drivers are deprecated.
Networking
The Network Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) version 5.0, 5.1, and 5.2 APIs are deprecated. New drivers for NDIS 6.0 must be written.
Hyper-V
The WMI rootvirtualization namespace is deprecated. The new namespace is rootvirtualizationv2.
Windows Authorization Manager (AzMan) is deprecated. You may need to use new management tools for virtual machines or redesign the authorization model.
Printing
The line printer daemon protocol (LPR/LPD) is deprecated. When this feature is eventually removed, clients that print to a server using this protocol, such as UNIX clients, will not be able to connect or print. Instead, UNIX clients should use IPP. Windows clients can connect to UNIX shared printers using the Windows Standard Port Monitor (see http://support.microsoft.com/kb/246868for more information).
Remote Data Service
The Remote Data service is deprecated. Migrate to the Windows Web Services API.
SMTP
SMTP and the associated management tools are deprecated. Though the functionality is still available in Windows Server 2012, you should begin using System.Net.Smtp. With this API, you will not be able to insert a message into a file for pickup; instead configure Web applications to connect on port 25 to another server using SMTP.
Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications
The Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications (SUA) is deprecated. If you use the SUA POSIX subsystem with this release, use Hyper-V to virtualize the server. If you use the tools provided by SUA, switch to Cygwin's POSIX emulation, or use either mingw-w64 (available from Sourceforge.net) or MinGW (available from MinGW.org) for doing a native port.
Transport protocols
The Transport Driver Interface (TDI) is deprecated. Use Windows Filtering Platform instead.
Layered Service Providers (LSP) are deprecated. Use Windows Filtering Platform instead.
Winsock Direct is deprecated. Use Network Direct instead.
SNMP
SNMP is deprecated. Instead, use the Common Information Model (CIM), which is supported by the WS-Management web services protocol and implemented as Windows Remote Management.
SQL Server
ODBC/OLEDB support for SQL is deprecated for versions beyond SQL Server 7 and SQL 2000. Migrate to SQL Native Client (SNAC) to use features provided by SQL Server 2005, SQL Server 2008, and later versions.
SQLXMLX is deprecated. Migrate code to use SQLXML.
Windows System Resource Manager
Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is deprecated. Similar functionality is provided by Hyper-V.
WMI providers
The WMI provider for Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is deprecated because the SNMP service is being deprecated.
The WMI provider for the Win32_ServerFeature API is deprecated.
The WMI provider for Active Directory is deprecated. Manage Active Directory with PowerShell cmdlets.
The WMI command-line tool (Wmic) is deprecated. Use PowerShell cmdlets instead.
The namespace for version 1.0 of WMI is deprecated. Prepare to adapt scripts for a revised namespace.
XML
Windows Server 2012 Tls Settings
XML-Data Reduced (XDR) schema elements are deprecated. Migrate Web applications that use this schema to the W3C Standards-compliant XML schema.
The XSL pattern feature of MSXML3 is deprecated. Migrate Web applications that use this feature to the W3C Standards-compliant XML Path Language (XPath) feature set.
Copyright
This document is provided “as-is”. Information and views expressed in this document, including URL and other Internet Web site references, may change without notice.
This document does not provide you with any legal rights to any intellectual property in any Microsoft product. You may copy and use this document for your internal, reference purposes.
©2012 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Microsoft, Active Directory, Hyper-V, MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT, Windows Server, and Windows Vista are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
This product contains graphics filter software; this software is based in part on the work of the Independent JPEG Group.
Windows Server 2012 Snmp Settings Download
All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
4.1